Qualcomm is announcing a couple of new addition to the existing 600 SoCs and 400 line up. Today’s announcement brings updated SoC with improved connectivity and digital signal processor. All of the new SoCs comes with the Hexagon DSP, Snapdragon X9 LTE modem (300 Mbps download and 150 Mbps upload), support Quick Charging 3.0, and Enhanced Voice Service (EVS) codec on VolTE calls.
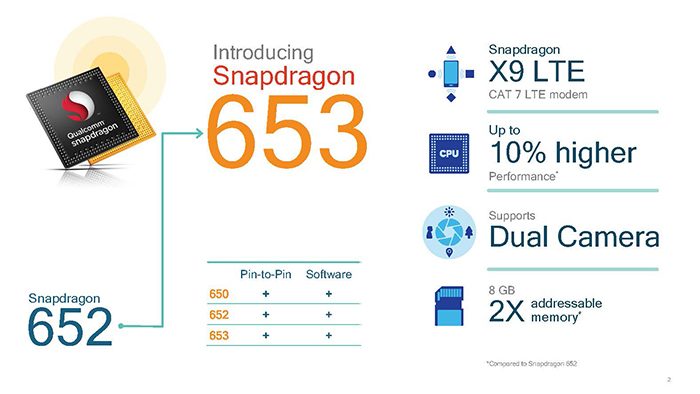
Starting with the new 653 SoC that is going to be the successor to the Snapdragon 652 which would be pin and software compatible with existing 650 and 625. The Snapdragon 653 is a 64-bit SoC is built on 28nm HPm process in big.Little CPU configuration (4 ARM Coretex A72 and 4 ARM Cortex A53) for a total of eight-cores. The GPU has not been updated and still uses Adreno 510. The performance boost is mainly due to the bump in the CPU clockspeed where the new SoC gets about 10% improvement over the Snapdragon 652. In addition to the performance boot, the SoC also is capable of supporting twice as much memory, up to 8GB. Furthermore, it gained dual camera support. Connectivity-wise, the SoC get an upgrade from the X8 LTE modem to the Qualcomm Snapdragon X9 LTE modem that support 2×20 MHz carrier aggregation for speed up to 300 Mbps down and 150 Mbps up.
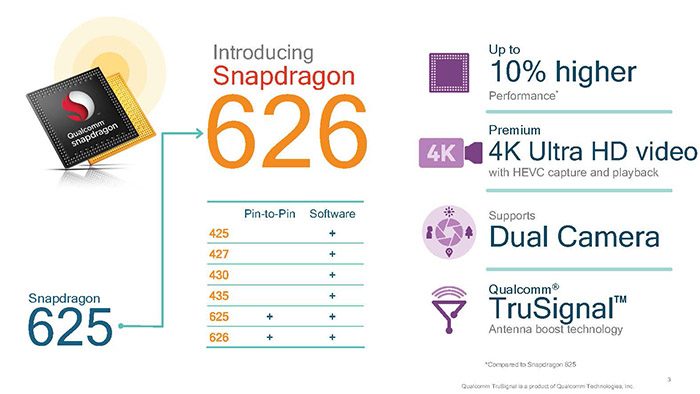
In addition to Snapdragon 653, Qualcomm also announced Snapdragon 626 that is pin-to-pin and software compatible with existing Snapdragon 625. Like the Snapdragon 625, the 626 SoC an octa-core Cortex-A53 with Adreno 506 that is built with 14 nm LPP process. The 626 gets roughly 10% performance boost (by higher clockspeed) and adds support for dual camera. Connectivity-wise, the 626 uses the same X9 LTE Modem as the 625 that that support 2×20 MHz carrier aggregation for speed up to 300 Mbps down and 150 Mbps up. However, the 626 get an upgrade to 4K Ultra HD video with HEVC capture and playback support and Qualcomm’s TruSignal antenna boost technology.
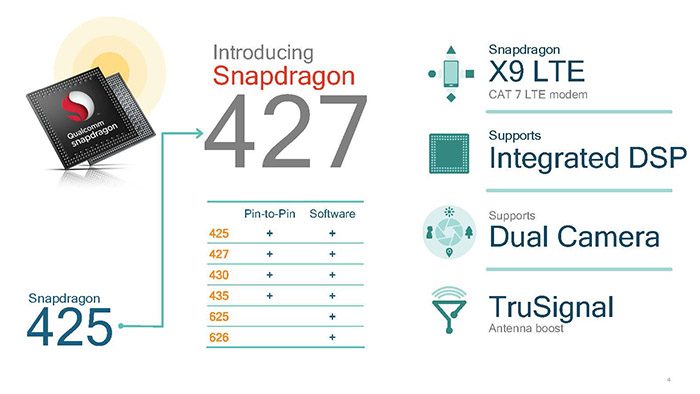
We also get a new SoC in the 400 series, the Snapdragon 427. The Snapdreagon 427 is pin-to-pin and software compatible with the existing 425, 430, and 435 SoCs. The Snapdragon 427 which also features X9 LTE (Cat 7) modem with integrated DSP, dual camera support and TruSignal antenna boost technology. While the 400 series SoCs are pin-to-pin compatible, the 427 is aimed for the 720p display devices whereas the 430/435 are aimed for the 1080p devices.
The Snapdragon 653 and 626 chipsets are expected to be commercially available by the end of 2016 whereas the Snapdraon 427 is expected to be available in devices in early 2017.
Qualcomm Sight for Connected Cameras

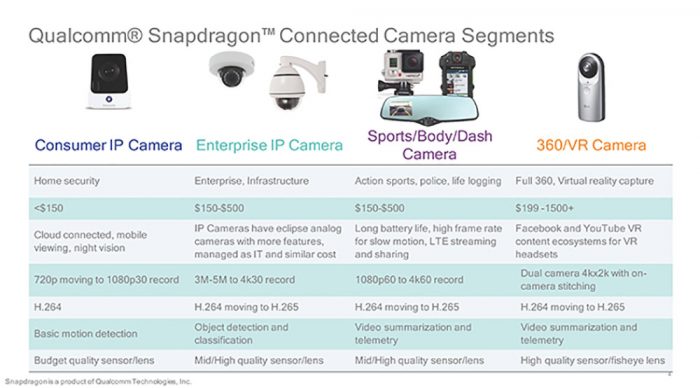
Today’s announcement also includes Qualcomm’s plan to enter the growing market of connected camera device. The Snapdragon Sight is the name of the new product portfolio. As Qualcomm points out, the streaming device is the growing market and Qualcomm wants to be SoC that powering these devices. Qualcomm’s press deck includes wide ranges of cameras that includes static camera such as IP camera to motion cameras such as sports cam, VR cam, and dash cam, body cam, etc. Qualcomm is leverage its SoC processing power and the cutting edge modem technology to provide best performance and connectivity.
The first product under the Connected Camera is the Snapdragon 625, a 14nm octa-core SoC clocked up to 2GHz with Andreno 506 GPU. The SoC supports 4K HEVC encoding capability for temporal noise reduction, video HDR, and 360 stitching. The SoC also supports heterogenous compute in order to combine its embedded DSP and GPGPU for deep learning video analytics. Additionally, it features the up to date connectivity with Snapdragon X9 LTE with 300 Mbps DL and 150 Mbps (CAT7), and WiFI support for b/g/n/ac and BT, so connectivity is not going to be an issue.
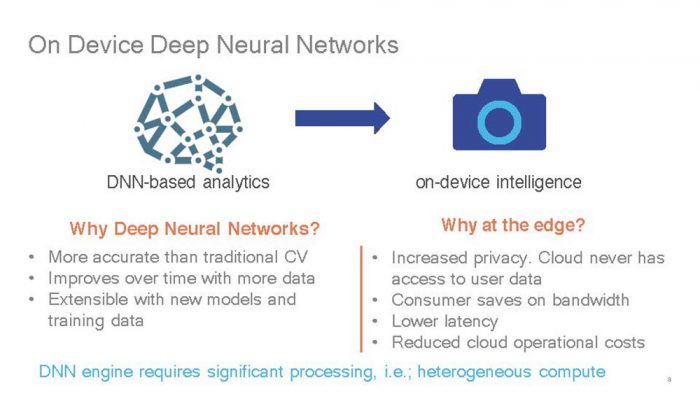
Additionally, Qualcomm highlights its SoC’s ability to handle on-device intelligence for video analytic to lower latency and reduce cloud operational costs. Also, Qualcomm points out its CPU along with support for heterogenous compute is capable of performing perform deep neural network analytics for better facial, object, and action recognition. Qualcomm provides the example of importance of deep neural network analytics that is able to distinguish not just between actions vs non-action but able to recognize important actions. For example, it is able to differentiate not just when a car is moving as oppose to parking but instead able to recognize that backup up as important action against other types of motion. To take advantage of the SoC’s feature, Qualcomm has released a video analytics manager API and connected camera Software Development Kit (SDK)
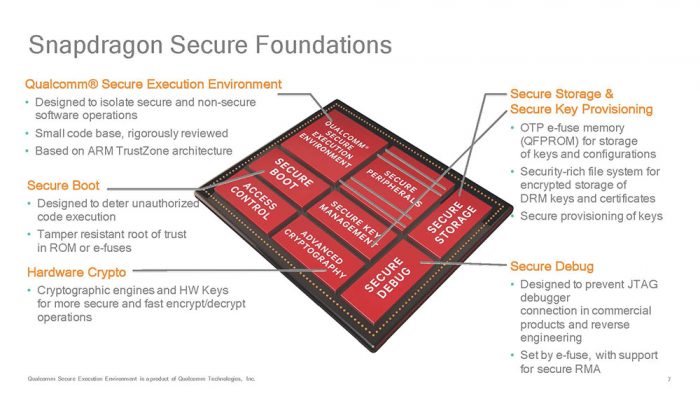
Qualcomm is especially proud of itself with the Snapdragon’s SoC’s security feature. Among them are the ARM TrustZone architecture, hardware encryption support, secure boot and secure storage.


The carrier have already begun testing the LTE-M where ATT is planning to pilot the LTE-M network in San Francisco market in November with commercial launch in 2017. Verizon ThingSpace IoT platform also will integrate Qualcomm MDM9206 modem that will be available for OEM integration in the early 2017.
 Bjorn3D.com Bjorn3d.com – Satisfying Your Daily Tech Cravings Since 1996
Bjorn3D.com Bjorn3d.com – Satisfying Your Daily Tech Cravings Since 1996