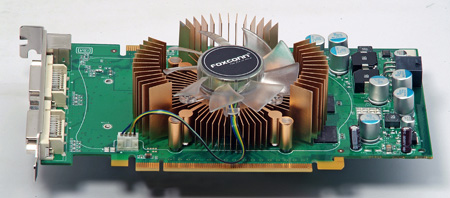
The 8600 GTS’s release has brought the DirectX 10 to the mainstream buyers. This new card from NVIDIA is not just a cut down version of its big brother, the 8800. Rather, it has packed a few extra features which are not found in the 8800. Check out our review to see what’s in the new card and how it performs as we will take a closer examination to the Foxconn’s 8600 GTS and compare it to the 7900 GT from Gigabyte.
INTRODUCTION
G84
|
Feature/Specification |
GeForce 8800 GTS |
GeForce 8800 GTS |
GeForce 8600 GTS | GeForce 8600 GT |
|
Processor
|
G80
|
G80
|
G84
|
G84 |
|
Fabrication Process
|
90nm
|
90nm
|
80nm
|
80nm |
|
Stream Processors
|
128
|
96
|
32
|
32 |
|
Core Clock (MHz)
|
575
|
500
|
675
|
540 |
|
Shader Clock (MHz)
|
1350
|
1200
|
1450
|
1190 |
|
Memory Clock (MHz)
|
900
|
800
|
1000
|
700 |
|
Memory Amount
|
768MB
|
648MB or 320MB
|
256MB
|
256MB |
|
Memory Interface
|
384-bit
|
320-bit
|
128-bit
|
128-bit |
|
Memory Bandwidth (GB/sec)
|
86.4
|
64
|
32
|
22.4 |
|
Texture Fill Rate (billion/sec)
|
36.8
|
24
|
10.8
|
8.64 |
FOXCONN
Foxconn is the registered trade name of Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd. Hon Hai is a global leader in providing mechanical and electromechanical solutions to the communications, consumer, and computer industries. The world’s largest manufacturer of PC connectors and enclosures, Hon Hai is also one of the world’s largest manufacturers of cable assemblies and motherboards – almost 40 million motherboards having been produced in 2005.Founded in 1974, and listed on the Taiwan stock exchange in 1991, Hon Hai has well in excess for 180,000 employees, is the largest private sector company in Taiwan, and is the largest exporter from mainland China. Market capitalization exceeds $18 billion USD. Sales in 2005 exceeded $28 billion USD.
Foxconn 8600 GTS
The card which Foxconn sends us is based on the NVIDIA’s reference design. In fact, it’s become the trend in the industry where major sellers simply use NVIDIA’s design on their cards and put their own sticker or graphic design on the heatsink and fan. However, Foxconn does inform us that the retail 8600 GTS should come with non-reference heatsink which should improve the cooling of the card for up to 15%. Unfortunately, we cannot verify the information since we do not have the retail card for testing.
The card comes in a very small package. This is the first mainstream graphics card that I have seen using this small packaging. The box is so small that it’s quite surprise; however I don’t mind the small package as that saves space and less trash for our environment. Ultimately, it’s the card that’s more important! If it performs well, I could care less about the packaging. This does not mean that Foxconn’s box is boring, rather the box has a nice graphics and is filled with features of the card on the back. Foxconn even puts a neat table on the back comparing the different graphics cards to give buyer some idea which card they should purchase for their particular need.





SYSTEM SETUP
|
System Configuration |
|
|
Processor |
Intel E6600 Core 2 Duo (stock speed) |
|
Motherboard |
EVGA nForce 680i SLI (BIOS P27) |
|
Memory |
Team Group TXDD2048M800HC4DC-D (2x1GB) |
|
Hard Drive |
Seagate Barracuda Barracuda 7200.10 SATA ST3400620AS (16MB cache) Western Digital WD2500KS-00MJB0 SATA (16MB cache) |
|
Graphics Cards |
EVGA 8800 GTX KO ACS3, ForceWare driver 158.19 Foxconn 8600 GTS, ForceWare driver 158.19 Gigabyte 7900 GT (GV-NX79T256DP-RH), ForceWare driver 93.71 |
|
Sound Card |
Creative X-FI (Driver 2.9.7) |
|
Power Supply |
NZXT 1000KW |
|
Operating System |
Windows XP SP2 |
| Chipset Driver |
ForceWare 9.53 |
I decided to put the Foxconn 8600 GTS against the last generation’s mid-range card, the 7900 GT (model GV-NX79T256DP-RH) and see if it’s worth upgrading your system to the new DX 10 capable graphics card. The Gigabyte 7900GT actually is overclocked to 525MHz/720MHz (core/memory). Just for fun, I threw in the 8800GTX KO ACS3 from EVGA to compare the performance difference between the cards.
Our fellow reviewer, Rob, has compared the 8600 GTS card with the 7900 GS. The 7900 GT and 7900 GS are fairly similar to each other. The 7900 GT is actually slightly older card than the 7900 GS but it has 8 vertex shaders compares to the 7 vertex shaders on the 7900 GS and 24 pixel shader compare to the 20 on the 7900 GS. The stock speed of the 7900 GS is actually faster than the 7900 GT but the Gigabyte card that was used in this test is factory overclocked to 525MHz for the core and 720MHz for the memory.
Note on the benchmark: Due to the instability of the EVGA 8800 GTX KO AC3, I had to downclock the speed to 600/980 for the test.
Here are the clock speeds of the cards that were used:
|
Feature/Specification |
Gigabyte 7900 GT |
Foxconn 8600 GTS |
EVGA 8800 GTX KO AC3 |
|
Core Speed (MHz)
|
525
|
675
|
600
|
|
Memory Speed (MHz)
|
720
|
600
|
980
|
Here is the list of testing softwares:
| Software | |
|
3Dmark06 v1.10
|
Default |
|
Company of Heroes.
SP Demo v1.5 |
Everything maxed out, 4xAA, 8xAF set in control panel |
|
FEAR v1.08
|
All Max, 4xAA, 8xAF |
|
Quake 4 v1.2: idnetdemo |
Max settings, 4xAA, 8AF |
|
Serius Sam II v2.070 |
Max settings, 4xA, 8AF |
PIXEL FILL RATE AND VERTEX SHADER POWER
Let’s start by looking at the pixel fill rate and vertex shader power of the 8600 GTS.
The texture fill rate of the 8600 GTS is not as high as the Gigabyte 7900 GT, especially the single texture. The gap has been narrowed with the multi-texturing. Looking at the data, we can see that the new architecture of NVIDIA’s 8 series graphics cards generally have better multitexturing fill rates than the last generation of cards.
The table has turned with the vertex shader performance. The 8600 GTS shines here. It significantly out-performs 7900 GT in both simple and complex shader and even out-performs 8800 GTX in simple shader.
The 8600 GTS trails the 7900 GT in the simple pixel shader benchmark, reminding us the limitation of the GPU. However, the unified architecture of the G84 allows it to proportion the amazing vertex shader ability we saw earlier into pixel shader when its needed. Looking at the Shader Particles and Perlin Noise benchmarks, we can see how the unified shader architecture is able to balance the pixel and vertex shader when render images. The 8600 GTS simply blows the 7900 GT away in the shader particle benchmark yet it is still able to keep up with the 7900 GT in the Perlin Noise benchmark.
3DMARKS06
After seeing the shader performance of the 8600 GTS, let’s look at how all the components come into play in rendering graphics. Let’s start by looking at the 3DMarks06.
3DMark06 developed by Futuremark is a synthetic benchmark used for universal testing of all graphics solutions. 3DMark06 features HDR rendering, complex HDR post processing, dynamic soft shadows for all objects, water shader with HDR refraction, HDR reflection, depth fog and Gerstner wave functions, realistic sky model with cloud blending, and approximately 5.4 million triangles and 8.8 million vertices; to name just a few. The measurement unit “3DMark” is intended to give a normalized mean for comparing different GPU/VPUs. It has been accepted as both a standard and a mandatory benchmark throughout the gaming world for measuring performance.
The 8600 GTS has a slight lead over 7900 GT. The 8600 GTS does not scale as good as the 7900 GT when the resolution is increased, thus narrowing the lead.
GAMING BENCHMARKS
The synthetic benchmarks really do not tell how the card will perform in games, so let’s take a look at the performance of some of more popular games on the market.
Company of Heroes
Company of Heroes(COH) is a Real Time Strategy(RTS) game for the PC. It is developed by the Canadian based company, Relic Entertainment, and published by THQ. We gladly changed from the first-person shooter based genres of the rest of our gaming benchmarks to this game which is RTS. Why? COH is an excellent game that is incredibly demanding on system resources thus making it an excellent benchmark. Like F.E.A.R. the game contains an integrated performance test that can be run to determine your system’s performance based on the graphical options you have chosen. It uses the same multi-staged performance ratings as does the F.E.A.R. test.
F.E.A.R
F.E.A.R. (First Encounter Assault Recon) is a first-person shooter game developed by Monolith Productions and released in October, 2005 for Windows. F.E.A.R. is one of the most resource intensive games in the FPS genre of games ever to be released. The game contains an integrated performance test that can be run to determine your system’s performance based on the graphical options you have chosen.
Quake 4
Quake4 was released to gaming world in 2005 the year after Doom 3 by Raven Software. It uses the highly touted Doom 3 engine in its operation which means it also functions with the OpenGL API during rendering. Quake 4 and Doom 3 are two highly valued benchmarks that have lost little popularity since their inception.
Serious Sam 2
Serious Sam 2 is a first-person shooter released in 2005 and is the sequel to the 2002 computer game Serious Sam. It was developed by Croteam using an updated version of their Serious Engine known as “Serious Engine 2”. We feel this game serves as an excellent benchmark which provides a variety of challenges for the the GPU/VPU you are testing. We once again automate the benchmarking process by using benchmarking software from HardwareOC to automate and refine the process.
Summary
In every gaming benchmark, we see that the 8600 GTS performs slightly worse than the souped up 7900 GT. When the resolution is low, the 7900 GT outperforms the 8600 GTS by quite a large margin, but the gap has been narrowed as the resolution is increased. This is opposite as what we have observed in the synthetic benchmark of 3DMark06. Although, both 8600 GTS and 7900 GT have almost linear performance loss with the increase in the resolution, we can see that the 8600 GTS’s performance seems to flatten out with the resolution at 1600×1200 and 1920×1200 while the 7900 GT keeps the linear performance drop.
OVERCLOCKING
The Foxconn 8600 GTS overclocks fairly well. I was able to overclock the card from the reference core/memory speed of 675MHz/1000MHz to 800MHz/1200MHz but the card was not stable enough to run any benchmark. I reduced the clockspeed slightly and was able to get a stable speed of 750 MHz/1150MHz. Let’s take a look at some benchmark results of the overclcok.
Unfortunately, even with overclocking, the Foxconn 8600 GTS is still not able to outperform the overclocked 7900 GT.
POWER CONSUMPTION
The 8600 GTS consumes approximately 20W more than the 7900 GT at idle but under load, both 7900 GT and 8600 GTS consume about the same wattage (with the 8600 GTS consuming 5W more than the 7900 GT). Both cards consume far less power (even under load) than the 8800 GTX at idle. Since it does not draw much more additional power compared to the last generation’s mid-range card, users would be safe to upgrade their system to the 8600 GTS without spending extra cash on a new power supply.
OPERATING TEMPERATURE
Foxconn’s 8600 GTS idle temperature is 55°C and load temperature is 75°C. It’s slightly hotter than I would have liked but it’s nothing to be alarmed about. One great thing about the 8600 GTS is the absolute near silence when it is under load. It’s good to hear that Foxconn is planning to put their own cooler on the card and it may even reduce the operating temperature and maybe reduce noise to an imperceptible level. Do keep in mind that the data is being presented with the reference cooler, not the Foxconn cooler. Also, the temperature of the 7900 GT is with Zalman’s cooler from Gigabyte rather than the NVIDIA reference cooler and the EVGA card has their own ACS3 cooler.
CONCLUSION
The NVIDIA 8600 GTS is a nice addition to the existing DirectX 10 graphic cards. With the release of the Windows Vista and the games that are coming in the near future, this means that DirectX 10 is here to stay. Although the NVIDIA 8600 GTS has been trimmed down quite significantly in the stream processor department compared to the 8800 GTX/GTS, its architecture design still makes it a great performer. We still do not know whether or not the slimmed down stream processor and 128-bit memory interface of the 8600 GTS will have any adverse effect on DirectX 10 games. However, it’s nice to see a mainstream DirectX 10 graphic card that is able to keep up with the last generation of card performance yet add new features such as improved PureVideo and HDCP.
The Foxconn 8600 GTS is a great graphic card for gamers who do not wish to spend an insane amount of dollars on the top of the line 8800 graphics card but still wish to have the performance and the newer technology. The card also overclcocks quite well even with the reference cooler, 750MHz/1150MHz (core/memory). Since Foxconn’s retail card will come with its own cooler, it may even be possible to achieve a higher overclock potential. In addition, the card’s power requirement is on par with the last generation’s graphic card, so no need to spend extra money upgrading the power supply. Furthermore, the Foxconn 8600 GTS comes with a nice bundles (useful programs, 2 DVI adapters, and HDTV/S-video converter) and three year warranty. The warranty period maybe slightly shorter compared to other manufactures but three years should be more than enough for most people.
Should you purchase the new 8600 GTS if you have already got a 7900 card? Well, the answer will probably depend on whether or not you need the added feature of the 8600. If your sole purpose is to play video games, then upgrading to the 8600 GTS would be somewhat of a down-grade in the performance, unless you need the DirectX 10 capability. However, none of the games currently on the market are DirextX 10 capable. For a gamer, it would be a better choice purchasing the 8800 series of cards intead of the 8600 cards or wait until the midrange AMD/ATI DirectX 10 graphic cards arrive in a few week before making your purchasing decision. However, if you have an entry level card and wish to upgrade to something better or if you need a card that can handle Vista better and have the ability to help rendering HD contents, then the Foxconn 8600 GTS would be a great choice without breaking your wallet.
Pros:
+ Single slot
+ New PureVideo to reduce CPU usage of HD content encoding
+ HDCP capable
+ Absolute silent
+ DirectX 10 Support
+ SLI capable
+ Nice bundle.
Cons:
– Not able to out-perform last generation’s midrange card, 7900 GT (overclocked)
– Slightly shorter warranty period (3 years)
– Slightly expensive
Summary
A good choice for a graphics card if you need a mid-range gaming card or the new features of the 8600. Otherwise, hold onto your exisiting card until the new AMD/ATI midrange graphic cards become available before you make your purchasing decision. The Foxconn 8600 GTS will receive a score of 7.5 (good) out of 10.
 Bjorn3D.com Bjorn3d.com – Satisfying Your Daily Tech Cravings Since 1996
Bjorn3D.com Bjorn3d.com – Satisfying Your Daily Tech Cravings Since 1996